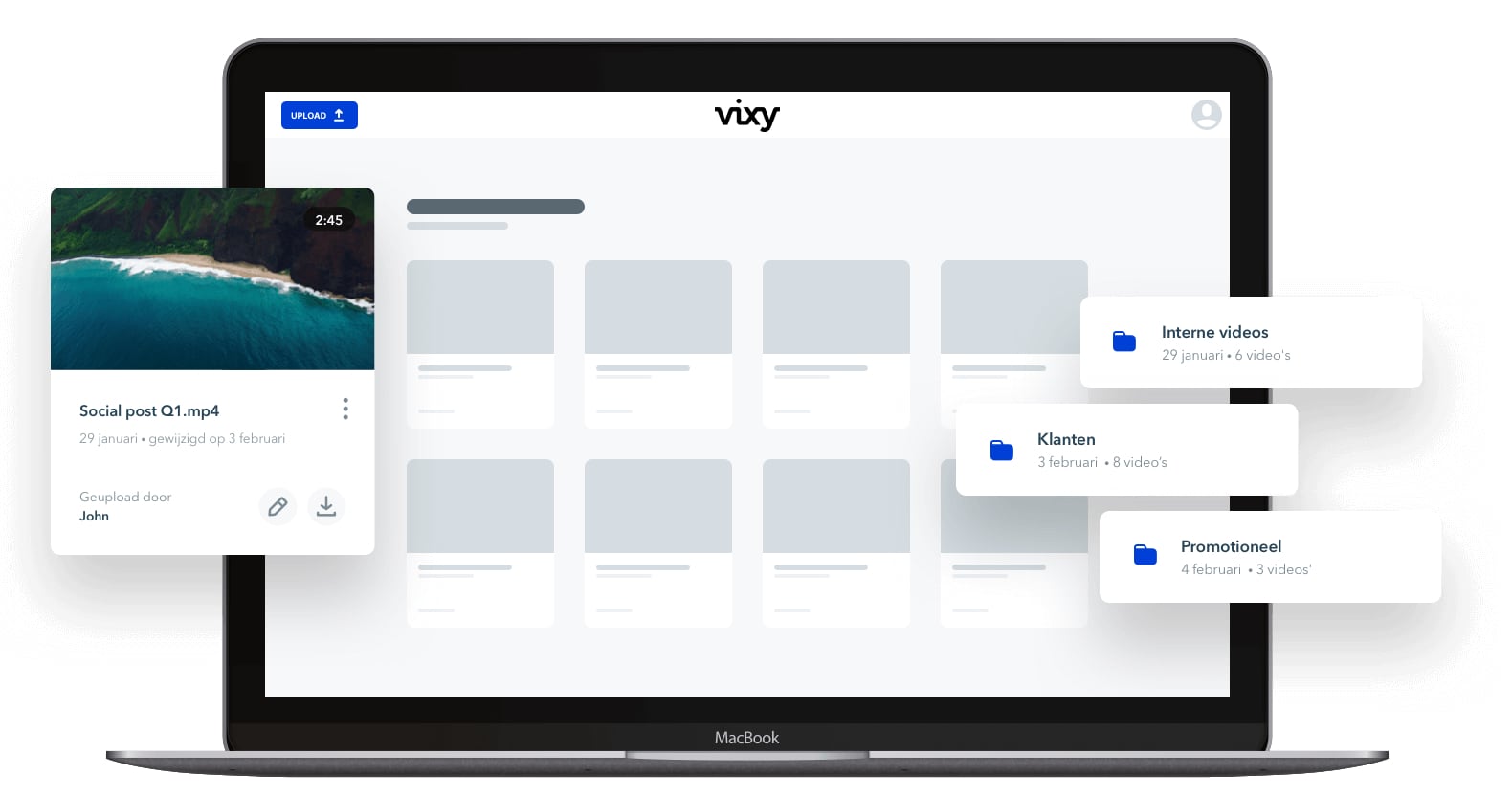
Video Hosting: choose a reliable and flexible platform..
A content delivery network (CDN) is a network of servers located strategically around the world to deliver web content faster and more efficiently. The majority of web traffic today is delivered through CDNs. With the right configuration, a CDN can also protect websites from online attacks.
For example if you were in Washington and wanted to view the website of your favorite store in Amsterdam that’s hosted on a server in the Netherlands, you would experience slow content load times if the request had to travel all the way across the Atlantic Ocean. To remedy this, a CDN would store a cached version of the Amsterdam website content in multiple geographical locations around the world, also called “points of presence” (PoPs). These PoPs contain their own caching servers and are responsible for delivering that content close to where you’re located in Washington.
CDN’s move content, data and applications closer to your users — at the edge of the network — to help your websites and apps perform faster, safer and at global scale.
What are the benefits of a content delivery network (CDN)?



